Elasticsearch生产环境配置
Elasticsearch在生产环境部署时候,我们需要考虑系统配置优化和Es本身配置优化,已达到能够发挥其最佳性能。本文是根据官方文档和个人工作实践总结出的生产环境配置。
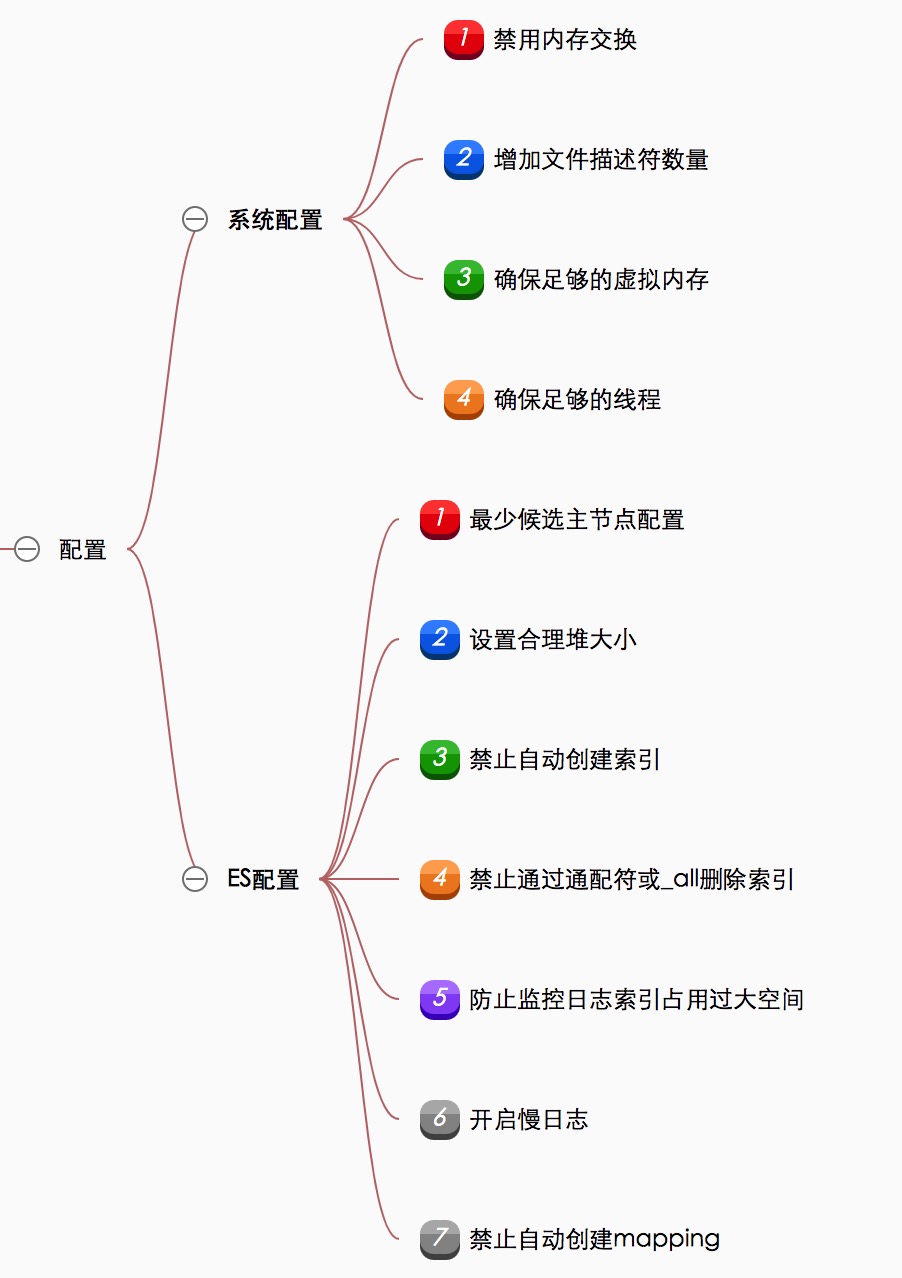
Elasticsearch在生产环境部署时候,我们需要考虑系统配置优化和Es本身配置优化,已达到能够发挥其最佳性能。本文是根据官方文档和个人工作实践总结出的生产环境配置。

Elasticsearch是基于JVM实现的,内存分配分为堆内(on-heap)和堆外(off-heapp)两部分。每部分的内存,可以用于不同目的的缓存,具体可以看下思维导图:
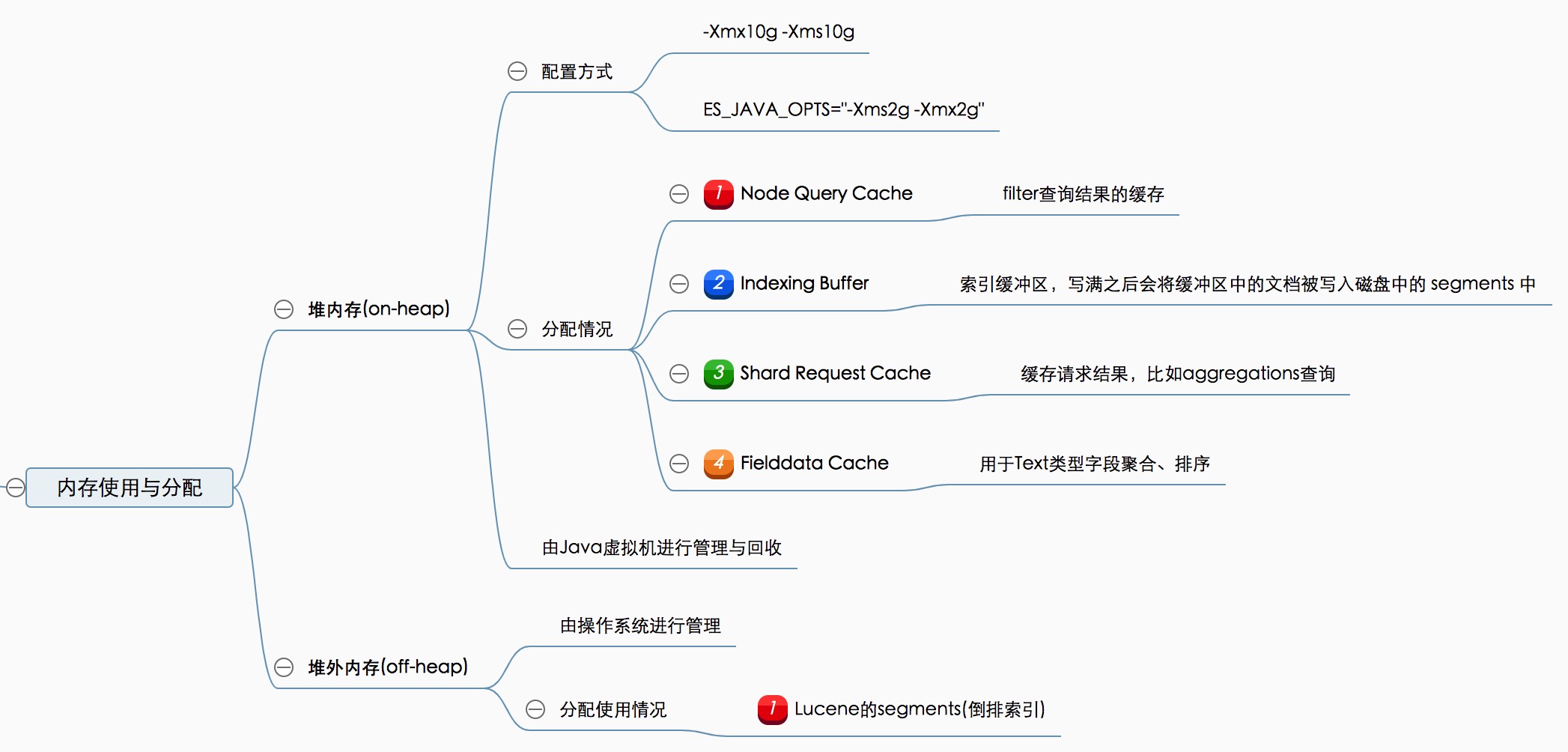
从整体来看如下所示:
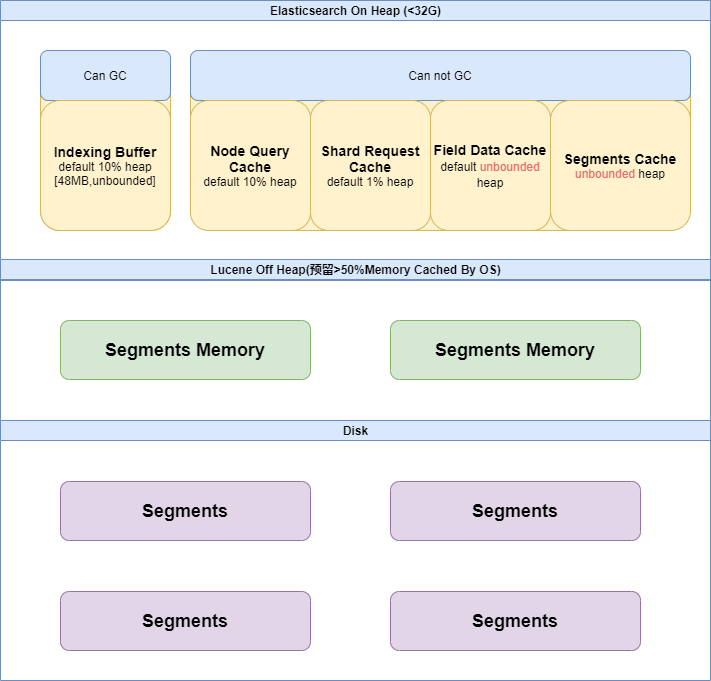
一般情况下,Java中分配的非空对象都是由Java虚拟机的垃圾收集器管理的,称为堆内内存(on-heap memory)。虚拟机会定期对垃圾内存进行回收,在某些特定的时间点,它会进行一次彻底的回收(full gc)。彻底回收时,垃圾收集器会对所有分配的堆内内存进行完整的扫描,这意味着一个重要的事实——这样一次垃圾收集对Java应用造成的影响,跟堆的大小是成正比的。过大的堆会影响Java应用的性能。
Java虚拟机的堆以外的内存,即直接收操作系统管理的内存属于堆外内存(off-heap memory),通过把内存对象分配在堆外内存中,可以保持一个较小的堆,可以减少垃圾回收对应用的影响。
注入攻击是OWASP总结的十大web安全风险中排在第一位的攻击形式, 而SQL注入(SQL Injection)攻击是注入攻击中最常见的一种形式。SQL注入漏洞可以从数据库读取敏感数据,修改数据库数据(插入/更新/删除),对数据库执行管理操作(例如关闭DBMS),恢复DBMS文件上存在的给定文件的内容系统,并在某些情况下向操作系统发出命令。
作为开发要防范这些攻击,就需要了解这些攻击方式。现列出Mysql数据库下几种常见SQL注入攻击示例,以作参考。

Elasticsearch是基于Apace Lunence构建的开源,分布式,具有高可用性和高拓展性的全文检索引擎。Elasticsearch具有开箱即用的特性,提供RESTful接口,是面向文档的数据库,文档存储格式为JSON,可以水平扩展至数以百计的服务器存储来实现处理PB级别的数据。
Elasticsearch可以快速存储,搜索,分析海量,索引数据速度达到毫秒级(近实时Near Real Time)。Github的代码搜索就是使用Elasticsearch来实现的。Elasticsearch使用场景有:
Lua诞生于1993年,是一种脚本语言,用C语言编写,其设计目的是为了快捷、高效嵌入到程序应用,比如Nginx服务器脚本。Redis从2.6.0版本开始内置Lua解释器,支持使用Eval命令运行Lua脚本。
在Redis中使用Lua脚本有两大特性:
原子性
Redis使用单个Lua解释器去运行所有脚本,当其在运行时,其他脚本或命令执行只能等待,这保证脚本已原子性方式运行。
高性能
Lua脚本一次可以执行多个redis命令,可以减少网络开销。对于较大脚本可以先使用SCRIPT LOAD 命令将其加载缓存中,然后使用EVALSHA运行近一步减少网络开销
安卓应用的版本信息分为版本名和版本号两部分。版本名是语义性版本,一般格式是主版本号.次版本号.修订版本号;版本号格式是数字。
应用新版本的版本号一定要旧版本要大,因为安卓系统在安装升级应用时候,会检查应用的版本号是否大于手机内已安装的该应用的版本号,若小于则直接拒绝升级此应用。
在开发需求中,有时候会需要根据应用的版本名进行筛选应用,比如筛选版本名大于7.33.1的Netflix应用,此时若直接把每个应用的版本名索引到es里面,然后根据版本名字段range范围查询,这是有问题的。比如12.8.1版本是高于7.31.1版本的,因为在es里面是按照字符串逐字比较的,导致出现相反结果。
9月份时候由于工作中涉及到大数据统计分析内容,研究了spark使用,10月份时候把研究内容在小组内简单做了一次分享。现在把分享的PPT贴出,分享过程中也涉及到真实项目使用spark演示,这部分为未贴出。

 原文地址:Comprehensive Introduction to Apache Spark, RDDs & Dataframes (using PySpark)
原文地址:Comprehensive Introduction to Apache Spark, RDDs & Dataframes (using PySpark)
Industry estimates that we are creating more than 2.5 Quintillion bytes of data every year.
Think of it for a moment – 1 Qunitillion = 1 Million Billion! Can you imagine how many drives / CDs / Blue-ray DVDs would be required to store them? It is difficult to imagine this scale of data generation even as a data science professional. While this pace of data generation is very exciting, it has created entirely new set of challenges and has forced us to find new ways to handle Big Huge data effectively.

原文地址:Using PySpark to perform Transformations and Actions on RDD
In my previous article, I introduced you to the basics of Apache Spark, different data representations (RDD / DataFrame / Dataset) and basics of operations (Transformation and Action). We even solved a machine learning problem from one of our past hackathons. In this article, I will continue from the place I left in my previous article. I will focus on manipulating RDD in PySpark by applying operations (Transformation and Actions).
As you would remember, a RDD (Resilient Distributed Database) is a collection of elements, that can be divided across multiple nodes in a cluster to run parallel processing. It is also a fault tolerant collection of elements, which means it can automatically recover from failures. RDD is immutable, i.e. once created, we can not change a RDD. So, then how do I apply operations on a RDD? Well, we apply an operation and store results in another RDD
For this article, one must have some understanding about Apache Spark and hands on experience in python programming.