定义
工厂方法模式(Factory Method Pattern)也称为工厂模式(Factory Pattern)。同简单工厂模式一样,工厂方法模式也是一种创建型设计模式。不同于简单工厂模式的都是通过同一个具体类(类的静态方法)或者函数来创建对象,工厂方法模式是通过一系列实现创建对象接口的具体子类来创建对象。即:
工厂方法模式定义一个用于创建对象的接口,让子类决定实例化哪一个类。Factory Method 使一个类的实例化延迟到其子类。
示例
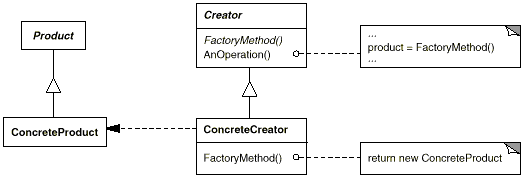
UML类图
实现
现在我们考虑实现一个各种图形svg格式绘制功能。首先我们先定义一个绘制接口IShape,接下来实现该接口的具体图形Circle和Rectangle。接着就是创建图形的接口IShapeFactory,以及实现该接口的具体工厂CircleFactory和RectangleFactory。
角色与代码映射
| 角色 |
代码 |
| Creator |
IShapeFactory |
| ConcreteCreator |
CircleFactory, RectangleFactory |
| Product |
IShape |
| ConcreteProduct |
Circle, Rectangle |
IShape
1
2
3
| type IShape interface {
Draw(io.Writer) error
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| type Circle struct {
Location Point
Radius float64
}
func (c *Circle) Draw(w io.Writer) error {
_, err := fmt.Fprintf(w, `<circle cx="%f" cy="%f" r="%f"/>`, c.Location.X, c.Location.Y, c.Radius)
return err
}
|
Rectangle
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| type Rectangle struct {
Location Point
Size Size
}
func (rect *Rectangle) Draw(w io.Writer) error {
_, err := fmt.Fprintf(w, `<rect x="%f" y="%f" width="%f" height="%f"/>`, rect.Location.X, rect.Location.Y, rect.Size.Width, rect.Size.Height)
return err
}
|
IShapeFactory
1
2
3
| type IShapeFactory interface {
Create(viewport Viewport) Shape
}
|
CircleFactory
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| type CircleFactory struct{}
func (factory *CircleFactory) Create(viewport Viewport) Shape {
return &Circle{
Location: viewport.Location,
Radius: math.Min(viewport.Size.Width, viewport.Size.Height),
}
}
|
RactangleFactory
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| type RactangleFactory struct{}
func (factory *RactangleFactory) Create(viewport Viewport) Shape {
return &Rectangle{
Location: viewport.Location,
Size: viewport.Size,
}
}
|
Document
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| type Point struct {
X float64
Y float64
}
type Size struct {
Width float64
Height float64
}
type Viewport struct {
Location Point
Size Size
}
type Document struct {
ShapeFactories []ShapeFactory
}
func (doc *Document) Draw(w io.Writer) error {
viewport := Viewport{
Location: Point{
X: 0,
Y: 0,
},
Size: Size{
Width: 640,
Height: 480,
},
}
if _, err := fmt.Fprintf(w, `<svg height="%f" width="%f">`, viewport.Size.Height, viewport.Size.Width); err != nil {
return err
}
for _, factory := range doc.ShapeFactories {
shape := factory.Create(viewport)
if err := shape.Draw(w); err != nil {
return err
}
}
_, err := fmt.Fprint(w, `</svg>`)
return err
}
doc := &svg.Document{
ShapeFactories: []svg.ShapeFactory{
&svg.CircleFactory{},
&svg.RactangleFactory{},
},
}
doc.Draw(os.Stdout)
|
总结
优点:可以避免创建者和具体产品之间的紧密耦合。
缺点:
- 每一个具体产品类就得需要一个对应的工厂,增加了代码的复杂度
参考
